Sustainability - Environmental Management
The Meiden Group is promoting environmental management that brings together business strategy and environmental activities.
We continually improve our environmental management system as we evaluate its adaptability and effectiveness.
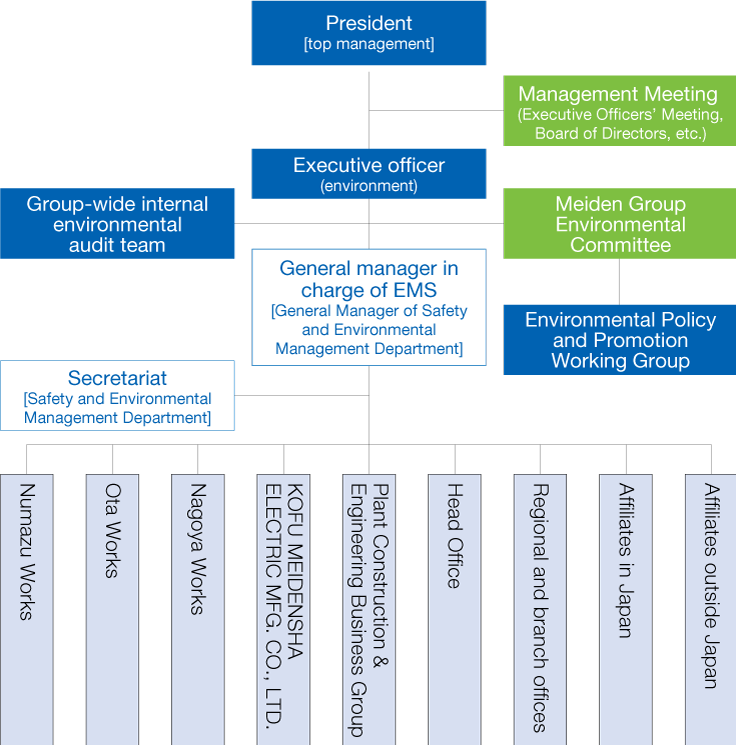
Under the leadership of the President, who is our chief executive officer, the executive officer (environment) oversees the environment management of the Meiden Group overall, while the general manager (GM) in charge of EMS works to maintain and improve the environmental management system (EMS).
In addition, our Group-Wide internal environmental audit team, an independent organization, audits environmental management initiatives, legal compliance, EMS effectiveness, and more, and offers ideas for improvement.
The executive officer (environment) chairs the Meiden Group Environmental Committee (MGEC), our highest decision-making body for environmental initiatives. The MGEC identifies issues to address, including risks relating to climate change and the like, sets environmental targets and formulates action plans, conducts management reviews, responds to emergency situations, reviews and reports on environmental measures and working groups (WGs), and sets environmental management policy directions.
For the most important issues, the executive officer (environment) and GM in charge of EMS consult with the Executive Officers’ Meeting, Board of Directors, and the like as needed and then act as decided by top management.
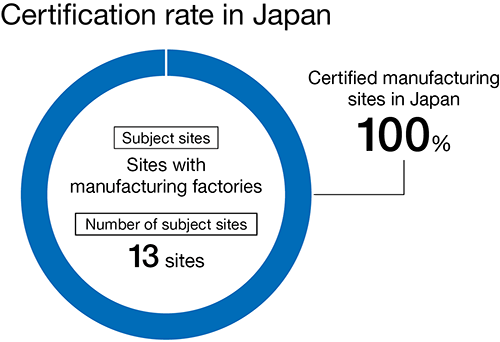
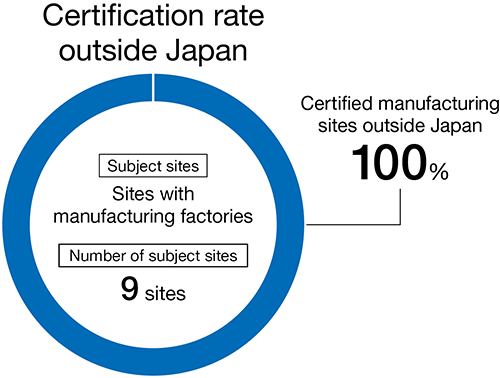
We are expanding the scope of bodies certified under ISO 14001, the international standard for environmental management systems. All 22 manufacturing sites in Japan and overseas have finished earning certification.
Subject locations within Group and percentage of those certified
We conduct internal environmental audits separate from the external audits we get from ISO 14001 registrars. Internal audits confirm the state of improvement on concerns pointed out in external audits and check up on audit items that are marked as priorities for that fiscal year.
In FY2023, our audits prioritized “environmental factors and evaluating environmental impact,” “matters related to the establishment, analysis, and evaluation of environmental targets,” “checks of compliance obligation initiatives,” “improving human resources,” and “legal requirements (laws on waste disposal and public cleansing and laws on curbing fluorocarbon emissions).” We determined that the Group was conforming to ISO 14001:2015 requirements overall and functioning effectively.
Additionally, we surveyed the state of our overseas manufacturing sites to examine applicable environmental improvement measures.
If any concerns are pointed out during internal environmental audits, we take them as an opportunity for improvement and incorporate them into further improvement initiatives.
The Meiden Group uses an “environmental information management system” that we put in place to manage and analyze environmental impact in our business activities.
The system collects and centrally manages information on environmental impact of business activities (such as automotive fuel, energy, waste, chemical substances, and water use) at Meiden Group manufacturing sites and offices, even those outside Japan.
The information so collected is used as basic data for efforts to lower environmental impact. It is also useful to ensure proper filings of information as required by the Act on Rationalizing Energy Use and Shifting to Non-fossil Energy, Act on Promotion of Global Warming Countermeasures, the electrical and electronic equipment industry’s “Carbon Neutrality Action Plan,” and Japanese PRTR system for reporting chemical releases and transfers.
Each Meiden Group work site and affiliated company sets and follows voluntary standards stricter than applicable laws and regulations. This ensures we remain in legal compliance. If a legal violation or incident does occur, our rules state that management shall be notified.
In FY2024, there was one incident involving standard values being exceeded and one incident of unprocessed wastewater entering a river. There were no serious violations of environmental laws or regulations (including water intake, wastewater, other waste, and harmful chemicals). We did not receive any complaints regarding noise or odor.
We quantify costs, etc., relating to environmental activities, with reference to the Ministry of the Environment’s “Environmental Accounting Guidelines 2005.”
The Meiden Group actively participates in the following industry groups and has declared our intention to decarbonize. The Meiden Group sees no disagreement or contradiction between its policies and directions on environmental issues and the policies and directions of these industry groups, and we are committed to furthering the initiatives of each.